Literature Review on Antibiotics
Abstract
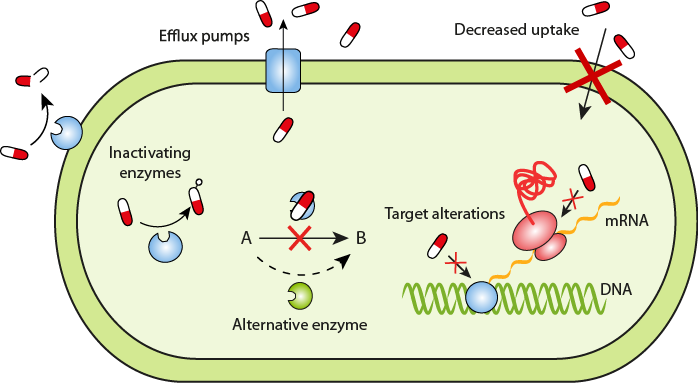
Antibiotics resistant capacity when pathogens are develops inhibition mechanisms in opposition to different antimicrobials that formerly sensitive. Different kinds of pathogens can advance resistance mechanisms or strategies via more than a few ways, such as natural or acquired. Innate resistance would be going on when pathogen can protects themselves from any drugs, this was once may be due to the capsules have low permeability to the pathogens. Additional reasons may be due to variations in the chemical compositio drug and the pathogens membrane structures. Acquired resistance potential the development of resistance of antibiotics that can be appear due to exceptional reasons, in this case the pathogen can beforehand inclined the tablets but through procedure they advance resistance mechanisms. The plasmids transformation, transduction, conjugation and transposition are the most common ways in which bacteria or pathogen can strengthen the resistance mechanisms.
References
Adams CL, Bonnett BN, Meek A H. (2000). Predictors of owner response to companion animal death in 177 clients from 14 practices in Ontario. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 217:
Al-Faham etal., (2011). Sale of antibiotics in Damascus. J infects Dev Ctries; 5(5):396-399.
Ardal, C., et al. (2015). International cooperation to improve access to and sustain effectiveness of antimicrobials. Lancet, 387(10015).
Bell, D.M., (2001). Promoting appropriate antimicrobial drug use: perspectives from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical Infectious Disease, 33(3).
Bergstrom K, Nyman G, Widgren S, Johnston C, Gronlund- Andersson U, Ransjo U. (2012). Infection prevention and control interventions in the first outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in an equine hospital in Sweden. Acta Vet Scand. 54:14.
Bilal Aslam Wei Wang Muhammad Imran Arshad Mohsin Khurshid, Saima Muzammil1 Muhammad Hidayat Rasool Muhammad Atif Nisar Ruman Farooq Alvi Muhammad Aamir Aslam Muhammad Usman Qamar Muhammad Khalid Farooq Salamat Zulqarnain B.(2018). Antibiotic resistance: a rundown of a global crisis. Infection and Drug Resistance, 11: 1648.
Bronzwaer, S.L., et al. (2002). A European study on the relationship between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance. Emerging Infectious Disease, 8(3).
Bryan J, Frank LA, Rohrbach BW, Burgette LJ, Cain CL, Bemis DA, (2012). Treatment outcome of dogs with meticillinresistant and meticillin-susceptible Staphylococcus pseudintermedius pyoderma. Vet Dermatol.23:361–8.
C. Lee Ventola, MS. (2015). The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis. Part 1: Causes and Threats. Vol. 40. 4,278.
Catry B, Van Duijkeren E, Pomba MC, Greko C, Moreno MA, Pyorala S., (2010). Reflection paper on MRSA in food-producing and companion animals: epidemiology and control options for human and animal health. Epidemiol Infect.138:626–44.
Conly, J.M., and Johnston, B.L. (2000). Antibiotic resistance in Canada at the dawn of the new millennium – a model for the developed world? Canadian Journal of Infectious Disease, 11(5).
Corley KT, Pearce G, Magdesian KG, Wilson WD, (2007). Bacteraemia in neonatal foals: clinicopathological differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative infections, and single organism and mixed infections. Equine Vet J. 39:84–9.
Dallap Schaer BL, Aceto H, Rankin SC, (2010). Outbreak of salmonellosis caused by Salmonella enterica serovar New port MDR-Amp C in a large animal veterinary teaching hospital. J Vet Intern Med.; 24:1138–46.
Ewers C, Bethe A, Semmler T, Guenther S, Wieler LH, 2012. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing and AmpC producing Escherichia coli from livestock and companion animals, and their putative impact on public health: a global perspective. Clin Microbiol Infect.; 18:646-55.
Fishman, N. (2006). Antimicrobial stewardship. American Journal of Infection Control, 34(5).
Foster JD, Trepanier LA, Ginn JA. (2014). Use of linezolid to treat MRSP bacteremia and discospondylitis in a dog. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc.50:53–8.
Friedman C.R. and Whitney C.G. (2008). It's time for a change in practice: Reducing antibiotic use can alter antibiotic resistance. Journal of Infectious Disease, 197(8).
Hanberger H, Diekema D, Fluit A, Jones R, Struelens M, Spencer R, Wolff M.(2001). Surveillance of antibiotic resistance in European ICUs. J Hosp Infect.; 48(3):161-76.
Hansen, M.P., et al. (2015). Antibiotic resistance: What are the opportunities for primary care in alleviating the crisis? Frontiers in Public Health, 3(35).
Hart, A., et al. (2006). Balancing acts: deciding for or against antibiotics in acute respiratory infections. Journal of Family Practice, 2006(55).
Holmes AH, Moore LSP, Sundsfjord A, Steinbakk M, Regmi S. (2016). Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 387(10014): 176-187.
Holmes, A.H., et al. (2015). Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet, 387(10014).
Loeffler A, Cobb MA, Bond R. (2011). Comparison of a chlorhexidine and a benzoyl peroxide shampoo as sole treatment in canine superficial pyoderma. Vet Rec.169:249.
Marshall BM, Levy SB. (2011). Food animals and antimicrobials: impacts on human health. Clin Microbiol Rev. 24(4):718-33.
Merrett GLB. (2013). Tackling antibiotic resistance for greater global health security. Chatham House.
Muras, M.K. (2013). A survey of patient behaviors and beliefs regarding antibiotic self-medication for respiratory tract infections in Poland. Archives of Medical Science, 9.
Nicholas Waglechner and Gerard D. W. (2017). Antibiotic resistance: it's bad, but why isn't it worse? BMC Biology, 15:84, 3.
O'Haire M. (2010). Companion animals and human health: benefits, challenges, and the road ahead. J Vet Behav. 5:226–34.
O'Neill, J. (2016). Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on antimicrobial resistance to the Government of the United Kingdom. HM Government, London.
Papich MG. (2013). Antibiotic treatment of resistant infections in small animals. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract.; 43:1091–107.
Pérez-Llarena, F. J., and Bou, G. (2016). Proteomics as a tool for studying bacterial virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Frontiers in microbiology, 7, 410.
Perreten V, Kadlec K, Schwarz S, Gronlund Andersson U, Finn M, Greko C. (2010). Clonal spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Europe and North America: an international multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother.65:1145–54.
Priest, P. (2001). Antibacterial prescribing and antibacterial resistance in English general practice: cross sectional study. British Medical Journal, 323(7320).
Public Health Agency of Canada (2015). Canadian antimicrobial resistance surveillance system report – 2015: protecting Canadians from illness. March 2015.
Ruscher C, Lubke-Becker A, Semmler T, Wleklinski CG, Paasch A, S. A. (2010). Wides pread rapid emergence of a distinct methicillin- and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus pseudo intermedius (MRSP) genetic lineage in Europe. Vet Microbiol; 144:340–6.
Sanath kumar and Manuel F. Varela, (2012).Biochemistry of Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps.Int J Mol Sci; 13(40):4486.
Seppala, H., et al. (1997). The effect of changes in the consumption of macrolide antibiotics on erythromycin resistance in group a streptococci in Finland. Finnish study group for antimicrobial resistance. New England Journal of Medicine, 337.
Shimels Tikuye Y. (2020). Review on Antibiotic Resistance: Resistance Mechanisms, Methods of Detection and Its Controlling Strategies. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res 24(5)-18652-18653.
Simpson, S.A., et al. (2007). General practitioner's perceptions of antimicrobial resistance: A qualitative study. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 59(2).
Stolle I, Prenger-Berninghoff E, Stamm I, Scheufen S, Hassdenteufel E, Guenther S. (2013). Emergence of OXA-48 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother.; 68: 2802–8.
Teixeira Rodrigues A. (2013). Understanding physician antibiotic prescribing behavior: a systematic review of qualitative studies. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 41.
The European pet food industry federation FEDIAF. (2012). Facts and Figures. Brussels. Available at http://www.fediaf.
The Societies for General Microbiology (SGS). 2015. Identification of bacterial Pathogens and anti-biotics resistance Mechanism. Ajo.prano terapia professionale.
Thomson K. (2010). Species specific and indication based use of antimicrobials in dogs, cats, cattle and horses in Finland - data collected using three different methods. Academic dissertation. Helsinki: Helsinki University printing house.
Thualfakar Hayder Hasan , Raad A. Al-H.(2020). Mechanisms of Antibiotics Resistance in Bacteria. Systematic Review Pharmacy Vol 11, Issue 6,818.
Van Duijkeren E, Catry B, Greko C, Moreno MA, Pomba MC, Pyorala S. (2011). Review on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudo intermedius. J Antimicrob Chemother.66:2705-14.
WHO (2014). Antimicrobial resistance Global Report on surveillance. Pp.69.
Wise, R. (2004). The relentless rise of resistance? Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 54.
World Health Organization ((WHO, 2011). Burden of endemic health care-associated infections worldwide.
World Health Organization ((WHO, 2014). Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on surveillance.
-
Article Viewed: 0
Total Download
##plugins.themes.ojsPlusA.frontend.article.downloadstatastics##