The Role of Environmental Microbiota in Bioremediation: Harnessing Bacteria for Pollutant Degradation
Clinical Medicine And Health Research Journal,
Vol. 5 No. 02 (2025),
12 April 2025
,
Page 1228-1240
https://doi.org/10.18535/cmhrj.v5i02.464
Abstract
Environmental pollution, driven by industrialization, urban expansion, and agricultural practices, has become a critical global concern, threatening ecosystems and public health. Conventional remediation techniques—such as chemical treatment, incineration, and excavation—are often expensive, energy-intensive, and environmentally disruptive. In contrast, bioremediation, which involves the use of microorganisms to degrade or neutralize pollutants, offers a sustainable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternative. Among the diverse microbial communities, environmental bacteria have emerged as key agents in this process due to their metabolic versatility and ability to adapt to a wide range of polluted environments.
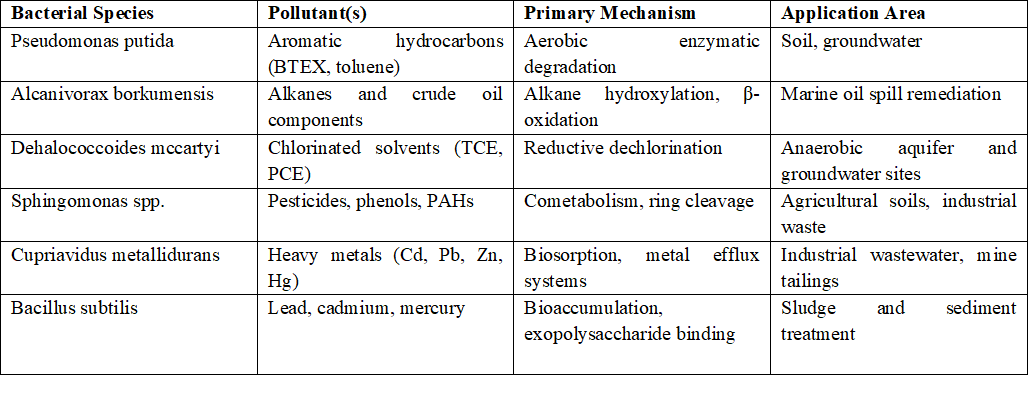
This study explores the pivotal role of environmental microbiota, with a focus on bacterial strains, in the degradation of pollutants such as petroleum hydrocarbons, chlorinated compounds, pesticides, and heavy metals. It provides a comprehensive review of bacterial mechanisms—including aerobic and anaerobic degradation, cometabolism, and biosorption—and highlights how specific bacterial species are tailored to target particular contaminants. A comparative table is presented to illustrate the functional relationships between bacteria and pollutant types, while a graph visualizes the degradation efficiency of selected bacterial strains over time.
Real-world case studies—such as the microbial response to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill and the degradation of industrial solvents—demonstrate the practical applications of bacterial bioremediation. While the approach offers numerous advantages, including ecological safety and scalability, it also faces challenges such as variability in microbial performance and site-specific limitations.
This paper concludes by emphasizing the potential of integrating microbial bioremediation with modern biotechnological tools like synthetic biology and metagenomics to enhance pollutant degradation. These strategies could lead to more robust, targeted, and efficient remediation processes in the future.
- Bioremediation, Environmental Microbiota, Bacteria, Pollutant Degradation, Hydrocarbons, Heavy Metals, Biosorption, Microbial Ecology
How to Cite
Download Citation
References
- Article Viewed: 0 Total Download


