Descriptive Statistical Study of The Number of Cases of Gastrointestinal Ulcers in Dhi Qar Governorate for The Year 2024
Clinical Medicine And Health Research Journal,
Vol. 5 No. 02 (2025),
25 March 2025
,
Page 1202-1209
https://doi.org/10.18535/cmhrj.v5i02.456
Abstract
Back ground: The importance of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) on a worldwide scale, highlighting its detrimental impacts on health and connections to elements like Helicobacter pylori infection and lifestyle choices. the necessity of preventative actions and all-encompassing management. This study is crucial to informing healthcare policy and activities in Dhi Qar since, despite international studies, there is still a dearth of understanding of PUD in the area. In order to provide information for clinical practices and public health initiatives, the study is to examine PUD prevalence, related factors, healthcare-seeking behavior, and awareness levels in the Dhi Qar population.
Methodology: Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) prevalence and related factors in Dhi Qar were examined in this cross-sectional study using a validated questionnaire that addressed the demographic criteria listed below. The sociodemographic attributes of age, gender, and place of residence. Clinical characteristics according to the location of the ulcer and infection with H. pylori. Behavioral factors or patients’ habits of smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol.A cross-sectional study was conducted at Al-Hasani Teaching Hospital in Dhi Qar in the Endoscopy Department during the period from 2/1/2024 to 12/1/2024.Descriptive statistical study of the number of cases of gastrointestinal ulcers in Dhi Qar Governorate where the number of patients admitted to the endoscopy. Adults 18 years of age or older who complained of dyspepsia and had an endoscopic evaluation in the endoscopy unit were included in the study. The flat was 1772, and both men and women were involved.
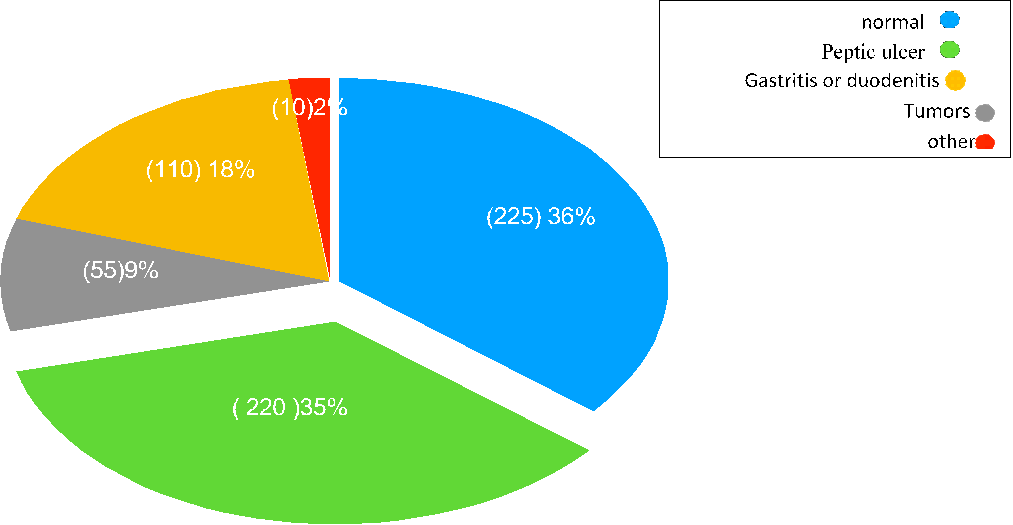
Results: The number of patients admitted to the department was 1772, the number of patients with peptic ulcers according to medical history, tests and endoscopy results was 620 patients with peptic ulcers during this study. The prevalence of peptic ulcers was no statistically significant differences were observed in the rates of digestive system diseases based on Age (P=0.31), Residential area (P=0.6), f Sex (P=0.3). While tatistically significant differences were observed in the rates of digestive system diseases based on Reason for referral (P=0.01), Level of education(P=0.01).
According to studies, smoking is one of the most important risk factors for the occurrence of ulcers, and because the number of smokers is less in society, the same applies to alcohol. Statistically significant differences were observed in the rates of digestive system diseases based on Status of Smoking, Source of drinking water, Hand washing habit before eating and Teeth decay (P=0.01). While no statistically significant differences were observed in the rates of digestive system diseases based on Fast Food, Chips and cakes (P=0.3). gastritis more prevalent infection 28%, Duodenitis recorded that 26% and Gastric ulcer 22%, while the lowest Duodenal ulcer rate recorded that 21%.
- H. pylori, gastrointestinal, Endoscopy, Peptic ulcer disease's, Gastritis, duodenitis
How to Cite
Download Citation
References
- Article Viewed: 0 Total Download


