Modification of The Bacterial Abundance Properties of Water by Immersed Non-Activated Charcoal
Abstract
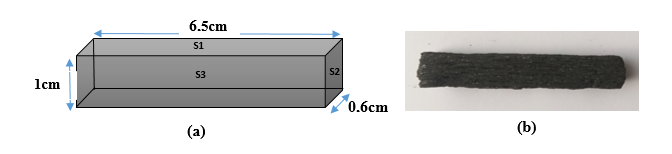
The present studies aim at reducing the planktonic bacterial load in drinking water using non-activated charcoal. The evaluation is dependent on the incubation time and the different physiological states of the bacterial cells. Three bacteria (Vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus) and two charcoal substrates (Okan and Tali) were used for the experimentation. The Bacteria adhered to charcoal fragments in varying degrees. Overall, the concentrations of fixed Vibrio cholerae reached 53.4x107 CFU/cm2 and 39.6x107 CFU/cm2 after 9 hours of contact in exponential phase on the Okan and Tali respectively. Those of fixed Staphylococcus aureus reached 5.8x106 CFU/cm2 after 3 hours of contact in exponential phase and 3.4x106 CFU/cm2 after 3 and 6 hours of contact in the same phase, on the Okan and the Tali, respectively. The highest abundances of Escherichia coli adhered to the charcoal fragments were 50.4x107 CFU/cm² on Okan and 53.2x107 CFU/cm² on Tali after 9 hours of contact in the exponential phase. The highest adsorption coefficient (639.06 adhered cells/cm2) was noted on Okan in the exponential phase with Vibrio cholerae cells; and the lowest (1.02 adhered cells/cm2) on Tali in stationary phase with Staphylococcus aureus. The incubation time significantly (P<0.01) influenced the adhesion of bacterial cells to charcoal substrates. Although the adsorption capacity and intensity of Okan were relatively higher, the comparison of the adsorption potential of the two substrates considered did not reveal any significant difference (P>0.05), reflecting the absence of the influence of the physical properties of these substrates on cell retention.
Keywords:
- Adhesion, bacteria, non-activated charcoal, contact duration, growth phases.
References
African Center for Advocacy, (2019). Access to water in Cameroon: a right or a privilege?
Ayarkwa J. & Owusu F.W., (2008). Cylicodiscus gabunensis Hams. In: Louppe D., Oteng-Amoako A.A. and Brink M. eds. Prota, 7(1): timbers/ bois d’oeuvre, 1. P. 188-202.
Beck G., Puchelle E., Plotkowski C. & Peslin R., (2001). Effect of growth on surface charge and hydrophobicity of Staphylococcus aureus. Annals of the Pasteur Institute/Microbiology, 139 (6). pp. 655-664.
Bouacherine S., (2013). Elimination of specific pollutants by adsorption on activated carbon and treated clay. Thesis of the master's degree from the University of Mohamed Cherif Messaadia-Souk-Ahras. P.96.
Boutaleb N., (2007). Study of the formation of biofilms on the surfaces of materials commonly used in drinking water pipes. Doctoral thesis from the University of Bretagne-Sud. P.194.
Branger A., Richer M. & Roustel S., (2007). Microchemistry and food. 2nd ed., Paris. P.337.
Center of Expertise in Environmental Analysis of Quebec, (2016). Search and enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus: membrane filtration method. MA.700-STA1.0, Rev.5, Ministry of Sustainable Development, the Environment and the Fight against Climate Change. P.18.
Da Silva A.K., Kavanagh O.V., Estes M.K. & Elimelech M., (2011). Adsorption and aggregation properties of norovirus GI and GII virus-like particles demonstrate 125 differing responses to solution chemistry. Environmental Science and Technology, 45. P. 520-526.
Dukam S., Pirion P. & Levi Y., (1995). Modeling the development of free and fixed bacterial biomasses in drinking water distribution networks. In: Adhesion of microorganisms to surfaces. P.149-160.
Eilers H., Pernthaler J., Glöckner F. & Amann R., (2000). In situ culture and abundance of North Sea pelagic bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66 (7). P. 3044-3051.
Fridjonsson E.O., Seymour J.D., Schultz L.N., Gerlach R., Cunningham A.B. & Codd S.L., (2011). NMR measurement of hydrodynamic dispersion in porous media subject to biofilm mediated precipitation reactions. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 121. P. 79-88.
Grasso D., Subramaniam K., Butkus M., Strevett K. & Bergendhal J., (2002). A review of non-DLVO interactions in environmental colloidal systems. Review in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 1. P. 17-38.
Guepi N., (2019). Cameroon: around 9 million people do not have access to drinking water, journal du Cameroun.com; published on March 22, 2019 at 4:01 p.m.; https://www.journalducameroun.com.
Haddouchi F., Lazouni H., Meziane A. & Benmansour A., (2009). Physicochemical and microbiological study of the essential oil of Thymus fontanesii Boiss et Reut. Africa Science, (5) 2. P. 246-259.
Hamadi F., Latrache H., Asserne F., Elabed S., Zahir H., Saad I.K., Hanine H. & Bengourram J., (2013). Quantitative adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus on stainless steel coated with milk. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 4. P. 299-304.
Holt J.G., Krieg N.R., Sneath P.H.A., Staley J.T. & Williams S.T., (2000). Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia. P.787.
Hounsou M.B., Agbossou E.K., Ahamide B. & Akponikpe I., (2010). Bacteriological quality of water in the Ouémé basin: case of total and fecal coliforms in the water reservoirs of Okpara, Djougou and Savalou in Benin. International Journal Biological Chemical Sciences, 4(2). pp. 377-390.
Ismahane, Guerradi A. & Hechachna, (2013). Industrial use of activated carbon: biological treatment; Amar Thladji University of Laghouat Algeria – Degree in Material Science. P.164.
Kendall K., Kendall M. & Rehfeldt F., (2011). Adhesion of cells, viruses and nanoparticles. Springer Dordrecht Heidelberg (Ed). P.282.
Kone T., (2012). Experimental study of the coupling between bacterial growth and transport of an organic pollutant in porous media. Doctorate/Ph.D thesis from the University of Lorraine. P.176.
Lemmens R.H., Louppe D. & Oteng-Amoako A.A., (2008). Lumber 2. Volume 2. P. 197.
Medema G.J., payment P., Dufour A., Robertson W., Waite M., Hunter P., Kirby R. & Anderson Y., (2003). Safe drinkink water: an on-going challenge in: Dufour et al. (Edition), Assessing Microbial safety of Drinking Water. Improving approaches and methods, World Health Organization, 92(4). pp. 154-630.
Moungang L.M., (2015). Adhesion of some bacteria of hygienic and health importance to rocky substrates immersed in well water: influence of abiotic factors. Thesis presented with a view to obtaining a Doctorate/Ph.D in Biology of Animal Organisms. P.207.
Nga N.E., (2016). Inventory and characterization of medicinal plants used therapeutically in the Sanaga Maritime department: Ndom, Ngambe and Pouma. Journal of Applied Biosciences, 106. P. 10333-10352.
Nikolaev Y.A., (2000). Role of long-range interactions in the regulation of adhesion of Pseudomonas fluorescens cells. Mikrobiologiya, 69. P. 356-361.
Noah E.O., Nola M., Moungang L., Noungang M., Krier F. & Nour-Eddine, (2011). Adhesion of Esherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa on rock surface in aquatic Microcom: Assessment of the influence of dissolved magnesium sulfate and monosodium phosphate. Environmental and Earth Sciences Research Journal, 3(4). pp. 364-374.
Nola M., Njiné T., Boutin C., Messouli M., Servais P., Foto Menbohan S., Ngo Bidjeck L.M., Zebaze T.S.H. & Kemka N., (2004). Retention of Escherichia coli from water infiltration in equatorial soil in Cameroon (Central Africa): The role of various soil layers. Journal of Cameroon Academy of Sciences, 2. P. 107-116.
WHO, (2004). Drinking Water Quality Guidelines (3rd ed). World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. P.12.
Pouneh K., (2009). Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation: evaluation of potential inhibitors of Quorum Sensing. Thesis Paul Sabatier University, Toulouse. P.328.
Rafael M., Mar C., Huq A. & Colwell R., (1996). Serogroup conversion of Vibrio cholerae non O1 to Vibrio cholerae O1: effect of growth state of cells, temperature and salinity.
Rodier J., Legube B. & Merlet N., (2009). Water analysis. 9th Edition. Dunod. P. 1600.
Samandoulgou I., (2015). Structural and functional study of the adhesion phenomenon of Noroviruses on inert surfaces and foods. Doctorate/Ph.D thesis from the University of LAVAL. P.157.
Tamsa A.A., (2017). Effect of the aqueous extract of the leaves of Eucalyptus microcorys Müller, 1860 on the culturability of some bacteria of health importance. Doctoral Ph.D thesis from the University of Yaoundé I. P. 237.
Vance D.B., (2002). Particulate transport in groundwater - part II. (http://:www.2the4.net/paartbact.html). (Accessed on December 13, 2004). P.12.
Vernhet E., (2005). Sedimentary processes, evolution, and paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the southern margin of the Ediacaran Yangtze platform (Doushantuo Formation, central China). PhD Thesis, Freie Universität at Berlin. P.175.
Vilaginès R., (2003). Water, environment and public health. Environmental and Earth Sciences Research Journal, Lavoisier ed., Paris. P.236.
-
Article Viewed: 0
Total Download
##plugins.themes.ojsPlusA.frontend.article.downloadstatastics##