Introduction to Different Diagrams Commonly Used in Literature
Clinical Medicine And Health Research Journal,
Vol. 4 No. 2 (2024),
3 April 2024
,
Page 858-865
https://doi.org/10.18535/cmhrj.v4i2.336
Abstract
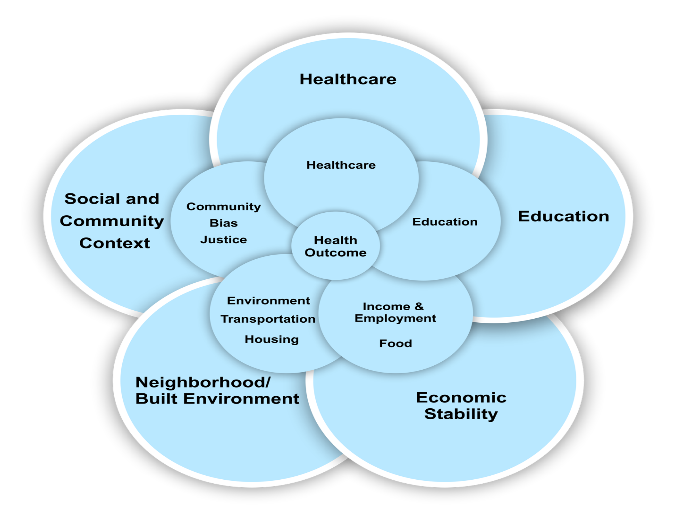
Diagrams help researchers and authors communicate and visualize complex concepts, data, and relationships effectively to a broader audience, including scientists, students, and the general public (Garcia-Retamero & Cokely, 2017). Visual representations can convey information more clearly and succinctly than paragraphs of text (Divecha et al., 2023; Duquia et al., 2014; Nguyen et al., 2021). Diagrams can take various forms, such as flowcharts, organizational charts, network diagrams, Venn diagrams, and others, and they are commonly used in various fields like business, engineering, science, education, and software development to illustrate processes, systems, relationships, and concepts. They help organize information, clarify relationships, identify patterns, and display data in an organized and visually attractive manner (Divecha et al., 2023; Duquia et al., 2014; Nguyen et al., 2021).
How to Cite
Download Citation
References
- Article Viewed: 0 Total Download


