Alveolar-Arterial Oxygen Gradient Ratio (GAaO2) As A Predictor of Early Mechanical Ventilation In A Patient with Suspected Sars Cov-2 Infection in the Adult Continuous Admission Area of The "Dr. Gaudencio González Garza” Of The La Raza National Medical Center.
Clinical Medicine And Health Research Journal,
Vol. 3 No. 5 (2023),
4 October 2023
,
Page 585-590
https://doi.org/10.18535/cmhrj.v3i5.248
Abstract
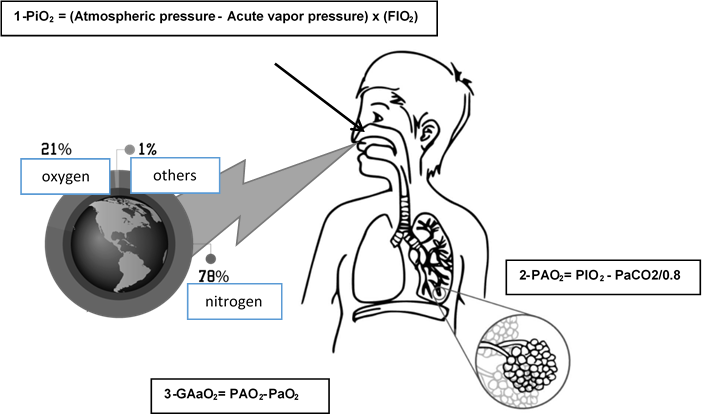
Background: Viruses and mainly COVID and the pneumonia it causes are among the pathologies that cause the greatest damage to the alveolus-capillary membrane of the lungs in patients with this disease.
Objectives: To relate the alveolar arterial oxygen gradient (GAaO2) and the start of early mechanical ventilation in patients with SARS COV - 2 virus infection in the continuous admission area.
Methodology: Descriptive, retrospective, observational, cross-sectional, with 165 clinical records of patients admitted to the emergency area in a period from April 2020 to 2021. Kolmogorov – Smirnov test, Mann-Whitney U and Pearson correlation coefficient were performed. with p>0.05, ROC curve for sensitivity and specificity with Youden index and multivariable regression analysis for correlation.
Results: A cut-off point of GAaO2 = 210.25 was obtained with sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 94%, with 2 times more risk of starting mechanical ventilation and correlation of 89%.
Conclusion: It was observed that the cut-off point was related to greater risk and correlation of initiation of mechanical ventilation. This is a reliable value to decide the start of invasive ventilation.
- SARS COV-2, arterial blood gas analysis, alveolar arterial oxygen gradient, mechanical ventilation, comorbidities
How to Cite
Download Citation
References
- Article Viewed: 0 Total Download


