Frequency of Surgical Site Infection in Emergency Appendicectomy for Complicated Appendicitis
Clinical Medicine And Health Research Journal,
Vol. 2 No. 5 (2022),
13 October 2022
,
Page 237-239
https://doi.org/10.18535/cmhrj.v2i5.104
Abstract
Objective: To find out the frequency of surgical site infections in emergency appendectomy for complicated appendicitis
Method: This cross-sectional study was conducted at Khyber Teaching Hospital, MTI, Peshawar from November 20, 2021 to August 12, 2022. We included 131 patients, who had undergone emergency appendectomy for complicated appendicitis. The sampling technique was consecutive non-probability sampling. Confidence interval of 95% and 7% margin of error were considered. The patients with complicated appendicitis on appendicect-omy were included in the study. Demographic data (age, gender), history of active smoking or diabetes mellitus at admission, procedure duration, appendicitis-type according to surgical findings (grossly inflamed, gangrenous, perforated), BMI were noted. All the data were collected on a proforma (Annex 1). SPSS software (version 23.0) was used for data analysis.
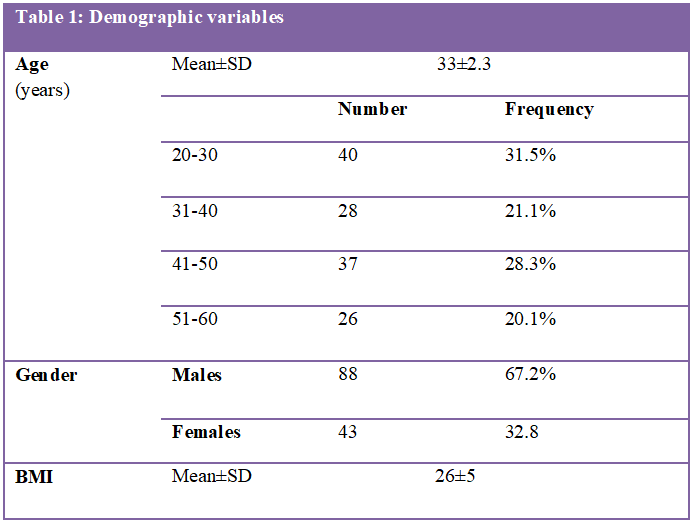
Results: Out of 131 patients, 88 (67.2%) were males and 43 (32.8%) were females with mean age of 33±2.3 years and mean BMI of 26±5. Frequency of surgical site infections among clean, clean-contaminated, contaminated, and dirty wound infections were 5/17 (29%), 20/67 (30%), 13/30 (43%), and 8/17 (49%) respectively. The overall frequency of surgical site infection was 46/131 (35%). Out of these 46 cases, 25 (54.3%) were superficial SSIs, 14 (30.4%) were deep SSIs and 07 (15.2%) were deep/space occupying SSIs.
Conclusion: In our study, the frequency of surgical site infections is 35% which is higher compared to other studies conducted. So proper preoperative and postoperative cares should be taken to decrease the frequency or incidence of surgical site infection in the department.
How to Cite
Download Citation
References
- Article Viewed: 0 Total Download


